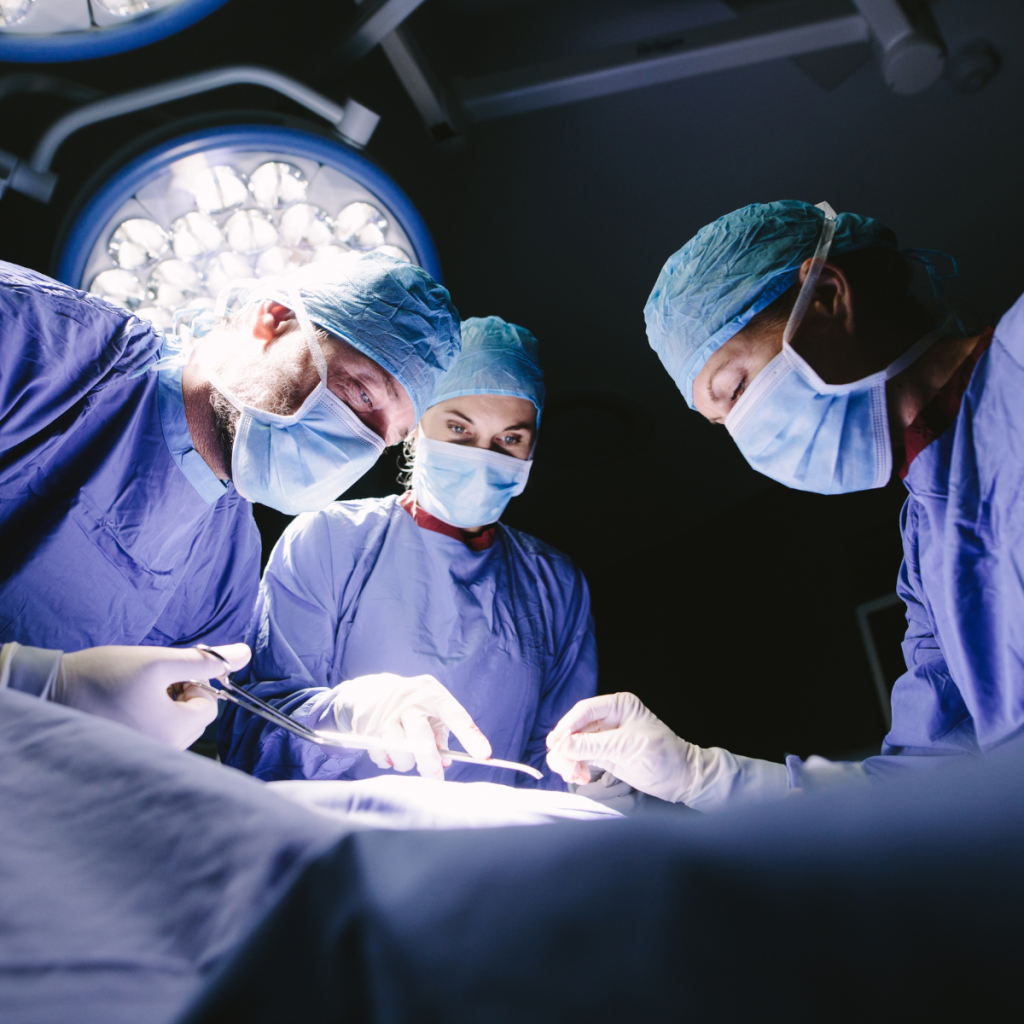
Where Do Surgical Technologists Work: A Comprehensive Guide
Discover where surgical technologists work and gain insights into their roles and responsibilities in various healthcare settings. Explore the diverse work environments that surgical technologists thrive in.
Surgical technologists play a crucial role in the operating room, supporting surgeons and other medical professionals during surgical procedures. Their expertise in preparing surgical instruments, sterilizing equipment, and ensuring a sterile environment contributes to the successful execution of surgeries. If you’re considering a career as a surgical technologist, it’s essential to understand the diverse work settings available in this field. In this article, we will explore where they work and provide valuable insights into the various environments they operate in.
- Hospital Operating Rooms
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- Specialty Clinics
- Labor and Delivery Units
- Emergency Rooms
- Trauma Centers
- Dental Offices
- Veterinary Hospitals
- Military Medical Facilities
- Educational Institutions
| Table of Contents |
|---|
| 1. Hospital Operating Rooms |
| 2. Ambulatory Surgical Centers |
| 3. Specialty Clinics |
| 4. Labor and Delivery Units |
| 5. Emergency Rooms |
| 6. Trauma Centers |
| 7. Dental Offices |
| 8. Veterinary Hospitals |
| 9. Military Medical Facilities |
| 10. Educational Institutions |
1. Hospital Operating Rooms
Hospital operating rooms are one of the primary work settings for surgical technologists. These rooms are equipped with state-of-the-art surgical equipment and technologies. They collaborate closely with surgeons, anesthesiologists, and nurses to ensure a smooth surgical experience for patients. Their responsibilities include preparing the operating room, arranging surgical instruments, and assisting with patient positioning.
2. Ambulatory Surgical Centers
Ambulatory surgical centers (ASCs) are healthcare facilities that focus on performing same-day surgical procedures. These centers provide a cost-effective alternative to hospitals for patients requiring minor surgeries. Surgical technologists working in ASCs assist surgeons in maintaining a sterile environment, preparing surgical instruments, and ensuring patient safety. ASCs offer a more relaxed and specialized work environment compared to hospitals.
3. Specialty Clinics
Surgical technologists can also find employment in specialty clinics, which cater to specific medical specialties such as ophthalmology, plastic surgery, or orthopedics. In these clinics, they assist physicians in specialized surgical procedures related to their respective fields. Working in a specialty clinic allows surgical technologists to gain expertise in specific surgical techniques and equipment.
4. Labor and Delivery Units
Labor and delivery units in hospitals require surgical technologists to be present during cesarean section deliveries. They assist the surgical team in preparing the operating room, arranging instruments, and ensuring a sterile environment for the safety of both the mother and the baby. They play a vital role in making sure the delivery proceeds smoothly and without complications.
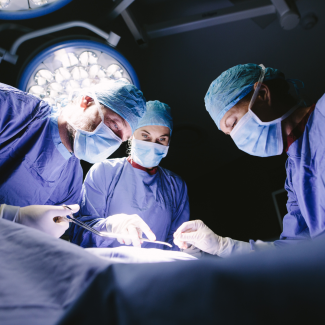
5. Emergency Rooms
Surgical technologists may be part of the emergency room team, particularly in cases that require immediate surgical intervention. They assist in emergency surgeries, such as trauma cases or life-threatening conditions. Their presence ensures that the surgical team has all the necessary instruments and equipment readily available to perform critical procedures promptly.
6. Trauma Centers
Trauma centers are specialized medical facilities that handle severe injuries and life-threatening emergencies. Surgical technologists in trauma centers work alongside trauma surgeons and other healthcare professionals to provide urgent surgical care to critically injured patients. Their ability to work under high-pressure situations and swiftly prepare the operating room is crucial in saving lives.
7. Dental Offices
Surgical technologists can find employment in dental offices where oral surgeries and procedures are performed. They assist dentists and oral surgeons in preparing the treatment room, sterilizing instruments, and ensuring patient comfort and safety. Dental offices provide a unique work environment interested in the field of dentistry.
8. Veterinary Hospitals
Surgical technologists can extend their skills to veterinary medicine by working in veterinary hospitals. They collaborate with veterinarians in surgical procedures for animals, ensuring proper sterilization of instruments and maintaining a sterile surgical environment. In veterinary hospitals, they contribute to the well-being and recovery of animals.
9. Military Medical Facilities
Military medical facilities offer diverse opportunities for surgical technologists. These facilities provide medical care to military personnel and their families. Surgical technologists in military medical facilities assist in a wide range of surgical procedures, from routine surgeries to emergency trauma care. They work in close-knit teams to ensure the health and well-being of military personnel.
10. Educational Institutions
Educational institutions such as vocational schools or colleges with surgical technology programs often employ experienced surgical technologists as instructors or clinical supervisors. In this role, surgical technologists share their knowledge and expertise with aspiring professionals, providing guidance and hands-on training. Working in educational institutions to contribute to the development of future healthcare professionals.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What qualifications are required to become a surgical technologist?
A1: To become a surgical technologist, you typically need a postsecondary certificate or an associate’s degree from an accredited surgical technology program. Some states may also require certification or licensure.
Q2: How much does a surgical technologist earn?
A2: The average annual salary varies depending on factors such as experience, location, and work setting. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for surgical technologists was $49,710 in May 2020.
Q3: What skills are essential for a surgical technologist?
A3: Important skills include attention to detail, manual dexterity, the ability to work well under pressure, strong communication skills, and a good understanding of surgical procedures and instruments.
Q4: Is there a high demand for surgical technologists?
A4: Yes, the demand is expected to grow in the coming years. Advancements in surgical procedures and an aging population contribute to the need for skilled surgical technologists in various healthcare settings.
Q5: Are there opportunities for career advancement as a surgical technologist?
A5: Surgical technologists can pursue additional certifications or degrees to advance their careers. With experience and further education, they can move into roles such as surgical first assistants or surgical technology instructors.
Q6: What are the typical working hours for surgical technologists?
A6: Surgical technologists often work full-time, and their schedules can vary depending on the healthcare facility. They may work day shifts, evenings, weekends, or be on call for emergency cases.
Q7: Is being a surgical technologist physically demanding?
A7: Yes, the role of a surgical technologist can be physically demanding as it involves standing for long periods, lifting and positioning patients, and handling surgical instruments and equipment.
Q8: Can surgical technologists specialize in a specific field?
A8: While surgical technologists can gain expertise in a specific field through experience, they are generally trained to assist in various surgical specialties. Specializations can occur naturally as they gain experience in a particular setting or work with specific surgeons.
Q9: What is the future outlook for surgical technologists?
A9: The future outlook for surgical technologists is promising, with a projected job growth of 7% from 2019 to 2029, which is faster than the average for all occupations. The demand for surgical technologists will continue to increase as the volume of surgeries performed rises.
Q10: How long does it take to become a surgical technologist?
A10: The time it takes can vary depending on the educational path chosen. Generally, completing a surgical technology program takes around 9 months to 2 years, while earning an associate’s degree can take approximately 2 years.
Q11: What is the role of a surgical technologist during surgery?
A11: During surgery, surgical technologists assist in preparing the operating room, ensuring the sterility of instruments and supplies, passing instruments to the surgeon and surgical team, and maintaining a clean and organized surgical environment.
Q12: Are surgical technologists allowed to assist in complex surgeries?
A12: Yes, surgical technologists are trained to assist in a wide range of surgical procedures, including complex surgeries. They work closely with the surgical team, providing necessary instruments and supplies, and anticipate the needs of the surgeons throughout the procedure.
Q13: Is it necessary for surgical technologists to be certified?
A13: While certification is not always mandatory, many employers prefer to hire certified surgical technologists. Certification can be obtained through organizations such as the National Board of Surgical Technology and Surgical Assisting (NBSTSA) by passing the Certified Surgical Technologist (CST) exam.
Q14: What are the prospects for career growth in the field of surgical technology?
A14: The field of surgical technology offers opportunities for career advancement and specialization. With additional experience and education, they can pursue roles such as surgical first assistants, surgical technology educators, or surgical technology program directors.
Please note that these FAQs and their answers are meant to provide general information and should not substitute for professional advice. If you have specific questions regarding your career or educational path as a surgical technologist, it’s recommended to consult with relevant authorities or professionals in the field.

Conclusion
Work in diverse healthcare settings, supporting surgical teams in delivering quality patient care. From hospital operating rooms to ambulatory surgical centers, specialty clinics, and beyond, they play an integral role in ensuring the success of surgical procedures. If you’re interested in pursuing a career as a surgical technologist, understanding the various work environments available will help you make informed decisions about your professional path. Remember to explore educational programs and certifications to enhance your skills and seize the exciting opportunities that lie ahead in this rewarding field.